why my wifi is not showing in laptop

Title: How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit
Channel: Howtosolveit
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit
why my wifi is not showing in laptop, why my wifi is not showing in laptop windows 11, why my wifi is not showing in laptop windows 10, why my wifi is not working in laptop, why my wifi network is not showing in laptop, why my wifi icon is not showing in laptop, why my wifi option is not showing in hp laptop, why my wifi is showing no internet in laptop, why 5g wifi is not showing in my laptop, why wifi is not showing in my dell laptop
WiFi MIA? Laptop Won't See Your Network?! (Solved!)
WiFi Woes? Your Laptop's Network Nightmare… Solved!
Have you ever found yourself staring blankly at your laptop, utterly bewildered? Your WiFi signal has vanished. The network icon stubbornly refuses to illuminate. Suddenly, you are disconnected from the digital world! It is frustrating, to say the least. Don’t despair! We have all been there at some point. Let's untangle this common tech headache.
The Vanishing Act: Diagnosing the WiFi Disappearance
First, take a deep breath. Panicking won’t help you. Instead, approach the problem methodically. Begin by checking the obvious. Is your router powered on? Are all the lights functioning correctly? Sometimes, a simple power cycle works wonders. Unplug your router and modem, wait a minute, then plug them back in. This often resolves minor glitches.
Next, scrutinize your laptop itself. Is WiFi enabled? Look for a dedicated WiFi key on your keyboard. It often has a symbol resembling radiating waves. Press it. Verify the WiFi switch is also in the "on" position. You will quickly rule out the most elementary issues.
Furthermore, consider other devices. Do other devices – your phone, tablet, or another computer – connect to your network? If they work perfectly fine, blame your laptop specifically. This narrows the scope of the problem considerably. Consequently, it's time to dive deeper.
Driver Dilemmas: The Silent Culprit
Outdated or corrupted network drivers are frequent culprits. Think of these drivers as the translators. They enable your laptop to communicate with your WiFi adapter. Outdated drivers can create communication breakdown. Follow these steps to update them:
- Open Device Manager. Search for it in your Windows search bar.
- Expand the "Network adapters" section.
- Locate your WiFi adapter (it might include words like "Wireless" or "WiFi").
- Right-click on it.
- Select "Update driver".
- Choose "Search automatically for drivers".
Windows will then search online for updated drivers. Let the system perform its magic. If this doesn’t work, try uninstalling the driver from the Device Manager. Afterward, restart your laptop. Windows should reinstall the driver automatically. As a result, this might fix your problem.
Network Settings Navigation: Reaching the Router
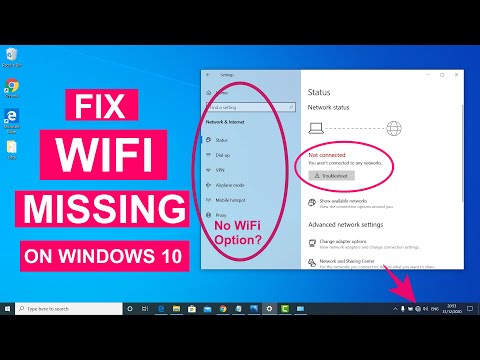
Sometimes, your laptop’s network settings are simply off. Let's ensure everything is configured correctly. You can reset your network settings. However, before you do this, consider the following:
- Go to your system settings.
- Select "Network & Internet".
- Choose "WiFi".
- Click "Manage known networks".
- Forget your network.
- Reconnect.
This eliminates any outdated settings. Also, check your IP address settings. They have the possibility of causing trouble. Ensure your IP address is set to "Obtain an IP address automatically". So, this allows your router to assign an IP address.
Router Rumble: Checking the Source
Your router itself may be the root of the issue. Consider whether other devices are experiencing similar problems. This can help determine whether the issue is the router or your laptop. Try these troubleshooting steps:
- Restart your router. This can often eliminate temporary network glitches.
- Check the router's firmware. Make sure it is up-to-date. Often, outdated firmware can cause connection issues.
- Examine your router's broadcast settings. Ensure your network is visible and not hidden.
If you're still struggling, consult your router's manual. Or, research the manufacturer's website. These resources offer specific troubleshooting advice. In short, don't be afraid to dig deeper.
Security Snafus: Firewall and Antivirus Interference
It's essential to protect your laptop. Firewalls and antivirus programs can occasionally cause connectivity problems. Think about it like this: overzealous security settings might block your WiFi connection. Temporarily disable your firewall and antivirus software. Then, attempt to connect to your network. If this resolves the problem, you'll need to adjust your security settings. Allow access for your WiFi adapter.
Hardware Hurdles: When the Problem Runs Deep
Sometimes, the problem lies in the hardware. Your WiFi adapter might be faulty. If you have an older laptop, it may need to be replaced. This is a more serious scenario. But, it is a possible cause. Consider contacting a professional for diagnosis and repair. It may be necessary to consider it.
Final Thoughts: Staying Connected
Losing your WiFi connection can be a frustrating experience. However, by following these steps, most users can resolve the issue. Begin with simple solutions. Then, gradually work your way through more complex troubleshooting steps. Try the suggestions above, you will be back online in no time. Good luck, and happy browsing!
**Blazing-Fast WiFi & Bluetooth: Upgrade Your Laptop NOW!**WiFi MIA? Laptop Won't See Your Network?! (Solved!)
Alright, let's be honest. We've all been there. You’re ready to binge-watch your favorite show, crush a work deadline, or just, you know, exist online, and… poof! Your laptop stares back at you with a blank, accusing look. The Wi-Fi? Vanished. Gone. MIA. It's like your network decided to play hide-and-seek and is winning spectacularly. But fear not, fellow digital travelers! We're going to dive deep into this frustrating phenomenon and, together, bring your Wi-Fi back from the abyss. Consider this your ultimate guide to conquering the Wi-Fi wilderness.
1. The Great Wi-Fi Disappearance: Why Did My Laptop Lose the Connection?
First things first: Why is this happening? Your laptop’s inability to see your Wi-Fi network can be a real head-scratcher, but it boils down to a few common culprits. Think of it like a faulty stage light; sometimes the issue is the bulb (your laptop), sometimes the wiring (your router), and sometimes… well, it’s just a bad connection. We’ll explore the most likely scenarios, from simple fixes to more involved troubleshooting.
2. Is It Really Just Your Laptop? A Quick Sanity Check
Before you start tearing your hair out (or, you know, throwing your laptop across the room – we’ve all been tempted!), pause. Take a breath. The first, and easiest, step is to determine if the problem is actually your laptop. Try these quick checks:
- Other Devices: Are your other devices (phone, tablet, smart TV) connecting to the Wi-Fi without a hitch? If they are, then the problem is very likely your laptop. If they aren't connecting, the issue probably resides with your router (more on that later!).
- The Obvious: Is the Wi-Fi button on your laptop on? I know, it sounds silly, but we've all done it. Sometimes it's just a switch, sometimes a function key combination (Fn + a key with a Wi-Fi symbol). Make sure it’s engaged.
- Airplane Mode: Is airplane mode enabled? This notoriously shuts down your Wi-Fi. Double-check this is turned OFF.
If other devices connect, and the aforementioned adjustments were made, we're on the right track. If not, we may need to inspect the router/internet provider.
3. Rebooting: The Universal Digital Panacea (and Why It Works)
Ah, the classic solution. The digital equivalent of "have you tried turning it off and on again?" It’s cliché, but it works more often than you’d think. We're talking about a simple reboot for both your laptop and your router. Think of it as giving your devices a clean slate. Here’s the drill:
- Laptop: Close everything, save your work, and restart your laptop. Give it a few minutes to boot up, then see if the Wi-Fi miraculously reappears.
- Router: Unplug your router and modem (if separate) from the power outlet. Wait a full 60 seconds. Seriously, give it time. Then, plug the modem back in. Once the modem is fully powered up (look for solid lights), plug the router in. Let it do its thing and then, try your laptop again.
- Why it works: Think of your router as a mini-computer. Sometimes, it needs a fresh start to clear out glitches and get back to its optimal state.
4. The Driver Dilemma: A Software Showdown
Now we're getting to the nitty-gritty. Think of drivers as translators. They help your laptop "speak" to your Wi-Fi adapter. If the translator is faulty, your laptop won't understand what the Wi-Fi router is saying. Driver issues can be a silent saboteur. Here’s how to troubleshoot:
Windows: Press the Windows key + X and select "Device Manager". Expand the "Network adapters" section.
- Look for your Wi-Fi adapter (it might be labeled something like "Wi-Fi," "Wireless Network Adapter," etc.).
- Are there any yellow exclamation marks or red X's? These are signs there's a problem.
- Right-click on your adapter.
- Update Driver: Select "Update Driver" and choose "Search automatically for drivers."
- Disable/Enable: If the driver update doesn't help, try disabling the adapter and then re-enabling it. This can sometimes reset the connection.
- Uninstall/Reinstall: If all else fails, right-click and "Uninstall" the driver, then restart your laptop. Windows will often reinstall a fresh driver on its own.
macOS: Click the Apple menu > "About This Mac" > "System Report". In the left sidebar, select "Wi-Fi." Look for any errors or warnings. macOS usually handles driver updates automatically, but you might need to update your operating system through System Preferences if you're having persistent issues.
5. The Network Adapter Blues: Hardware Woes and Basic Troubleshooting
Sometimes, even perfectly updated drivers can't fix a hardware problem. Your Wi-Fi adapter in your laptop might be faulty. This is rarer, but still possible.
- Run Troubleshooter: Windows has a built-in network troubleshooter. Search for "Troubleshoot settings" > "Network and Internet" > "Network troubleshooter." Let it run and see if it detects and fixes any problems.
- Check the Physical Connection (If Applicable): Some laptops have a physical button or switch to enable/disable the Wi-Fi adapter. Make sure it's in the "on" position.
- Internal Adapter Fault: If using an internal adapter, and if you have the expertise, you can cautiously open your device (but be very careful), and check the physical connections. If you are uncomfortable working with the internal components, consider professional repair.
6. Router Range Restrictions: Are You Too Far Away?
Think of your router as a radio station. The further you are from the transmitter (the router), the weaker the signal. Your laptop might be struggling to "hear" the Wi-Fi.
- Proximity Test: Try moving your laptop closer to your router. If the Wi-Fi miraculously appears, you've identified a range issue.
- Obstacles: Thick walls, metal objects, and other electronics can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Move your router to a more central, open location.
- Signal Boosters/Mesh Networks: Consider a Wi-Fi extender or a mesh network if you need to improve coverage throughout your home or office.
7. Security Settings Shenanigans: Password Problems and Network Name Nonsense
Incorrect network passwords, hidden networks, and other security settings can also play havoc on your connection attempts.
- Double-Check Your Password: This sounds obvious, but mistyping your Wi-Fi password is a common culprit. Make sure you're entering the correct password, and that Caps Lock isn’t accidentally on.
- Hidden Networks: If your Wi-Fi network is hidden (meaning it doesn’t broadcast its name), you'll need to manually add the network to your laptop. You’ll need the network name (SSID) and the security type (WPA2, WPA3, etc.) and the password.
- Router Security Settings: Check your router's configuration (usually accessed via your web browser by typing in the router's IP address, often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Make sure your security settings are up-to-date and compatible with your laptop's capabilities.
8. Router Channel Congestion: Too Many Signals, Too Few Channels
Think of Wi-Fi channels like lanes on a highway. If too many devices are using the same lane (channel), it can cause traffic congestion (slow speeds and dropped connections).
- Access Your Router's Settings: Log into your router's settings (as described in Section 7).
- Change the Channel: Look for the Wi-Fi channel settings. Try experimenting with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are usually good starting points, as they are less congested).
- Channel Width: Experiment with 20MHz and 40MHz settings (or 80MHz if your router supports it).
9. Firewall Follies: Blocking the Wi-Fi Flow
Your laptop's firewall (and sometimes your security software) can sometimes block Wi-Fi connections.
- Temporarily Disable the Firewall: As a test, temporarily disable your firewall. Then, try connecting to the Wi-Fi. Be cautious when disabling your firewall, as it can make your computer vulnerable.
- Check Firewall Rules: If disabling the firewall fixes the problem, you'll need to create an exception in your firewall rules to allow your laptop to connect to your Wi-Fi network. Consult your firewall's documentation for instructions.
- Software Conflicts: Sometimes, security software can interfere with your Wi-Fi. Try temporarily disabling your security software to see if it resolves the issue.
10.
Download This ONE Weird Trick To Get Blazing Fast Laptop WiFi!Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
By Sandeep Singh Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
Fix Wi-Fi Icon Not Showing Problem on Windows 1110 - 2025 FIX

By Crown GEEK Fix Wi-Fi Icon Not Showing Problem on Windows 1110 - 2025 FIX by Crown GEEK
Fix WiFi Icon Not Showing Problem on Windows 11 How To Fix WiFi Not Working On Windows 11 2025

By WinLozy Fix WiFi Icon Not Showing Problem on Windows 11 How To Fix WiFi Not Working On Windows 11 2025 by WinLozy

Title: How to solve Wi-Fi Not showing Problem in Windows 10 200 Fixed
Channel: Rounak Verma
How to solve Wi-Fi Not showing Problem in Windows 10 200 Fixed by Rounak Verma
Wifi Not Found
WiFi MIA? Laptop Won't See Your Network?! (Solved!)
Navigating the digital world hinges on a reliable WiFi connection. There's nothing more frustrating than your laptop suddenly refusing to acknowledge the presence of your home network. The blinking WiFi icon, the ominous "no internet" message – these are all too familiar indicators of a frustrating digital impasse. But before you succumb to the despair of a device-less existence, take heart. In the event your laptop’s WiFi has gone AWOL, consider the following comprehensive guide to troubleshoot and resolve the issue, restoring your connectivity and your peace of mind.
Initial Diagnosis: Pinpointing the Source of the Disconnection
Before launching into a series of troubleshooting steps, it's crucial to establish the scope of the problem. Is the lack of a WiFi connection specific to your laptop, or are other devices in your household experiencing the same issue? Try connecting a smartphone, another laptop, or a tablet to your WiFi network. If these devices can connect without issue, the problem likely originates within your laptop itself. However, if all devices are unable to access the internet, the issue is more likely stemming from your router or internet service provider. This initial assessment will steer the troubleshooting process in the right direction.
Laptop-Specific Troubleshooting: A Detailed Guide
Assuming that your laptop is the sole device experiencing the WiFi blackout, the following steps offer a systematic approach to reclaiming your connection:
1. The Airplane Mode Fiasco:
One of the simplest, yet most common, culprits for WiFi unavailability is the accidental (or not-so-accidental) activation of Airplane Mode. This feature disables all wireless communication, including WiFi. Locate the Airplane Mode toggle on your laptop. This can usually be found in the system tray (bottom right corner of your screen), in the settings menu (accessed via the Windows icon or the Apple menu), or by pressing a dedicated function key (often denoted by an airplane icon) on your keyboard. Ensure that Airplane Mode is deactivated. If enabled, click the toggle to disable it.
2. The WiFi Adapter Shuffle: Ensuring the Driver is Working
Your laptop relies on a WiFi adapter, a physical component that translates wireless signals into data your computer can understand. Problems with the adapter's driver – the software that enables the adapter to communicate with your operating system – are a frequent cause of connectivity issues.
Driver Verification: Open the Device Manager. In Windows, you can typically do this by searching for "Device Manager" in the Start menu. On a Mac, use the "About This Mac" option from the Apple menu, followed by "System Report."
Locating the Network Adapter: In the Device Manager, look for the "Network Adapters" section. Expand this section to reveal your WiFi adapter (it may be labeled as "Wireless Network Adapter," "Wi-Fi Adapter," or something similar).
Driver Status Check: Verify the status of your WiFi adapter. A yellow exclamation mark or red "X" next to the adapter icon indicates a problem. If present, right-click on the adapter and select "Properties." The "Device status" within the properties window will offer more details about the issue.
Driver Update: If the driver is outdated or experiencing problems, right-click on the adapter and choose "Update driver." Select "Search automatically for drivers" and allow Windows or macOS to search for and install the latest driver version. In some instances, you may need to download the latest driver directly from the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, etc.) for your specific adapter model.
Driver Reinstallation: If updating the driver doesn't solve the problem, you can try uninstalling and reinstalling it. Right-click on the adapter, select "Uninstall device," and follow the prompts. Then, restart your laptop. Upon restarting, the operating system should automatically attempt to reinstall the driver. Alternatively, you can manually reinstall the driver using a previously downloaded version.
3. The Network Reset: For a Fresh Connection
Resetting your network settings can often resolve underlying software conflicts that might be hindering WiFi functionality.
- Windows Network Reset: In Windows 10 and 11, you can perform a network reset through the Settings app. Navigate to "Network & Internet," then "Status," and finally, click on "Network reset" at the bottom of the page. Follow the on-screen instructions. This will reset your network adapters and related settings to their default values.
- Mac Network Reset (Simplified): macOS does not have a dedicated “reset” option in the same manner as Windows. The most effective ways of achieving a similar outcome are to renew the DHCP lease and to delete and re-add the WiFi network to your preferred networks.
- Renewing DHCP Lease: Open System Preferences > Network, select your Wi-Fi adapter, and click "Advanced." Select the "TCP/IP" tab and click the "Renew DHCP Lease" button. This prompts your computer to request a new IP address from your router.
- Deleting and Re-Adding the Network: Return to the Network window, select your Wi-Fi adapter, and click "Advanced." In the “Preferred Networks” tab, select your home Wi-Fi network and click the minus (-) button to remove it from the list. Click "OK" and then "Apply" and try reconnecting to your Wi-Fi network.
4. The Manual Connection: A Direct Approach
Sometimes, your laptop may simply fail to automatically connect to your network. Manually entering your network's SSID (the network name) and password can sometimes bypass these glitches.
- Windows: Click the WiFi icon in the system tray. Click on "Network & Internet settings" and then "Manage known networks". Find your network click, "Forget". Then, click the WiFi icon again and select "Connect." Choose your network from the list and enter your password.
- macOS: Click on the WiFi icon in the menu bar. Select "Join Other Network…" Enter the SSID (network name), select the security type (usually WPA2/WPA3 Personal), and enter your password.
5. Hardware Considerations: Physical Checks and Maintenance
Rarely, the issue might relate to the physical components of your laptop. While less common, these aspects deserve consideration:
- WiFi Adapter Disablement: Double-check your laptop's physical switches. Some laptops have a physical switch or function key (often alongside other function keys like brightness controls) to enable or disable the WiFi adapter. Ensure the switch is in the "on" position.
- Antenna Placement: Keep your laptop away from significant obstructions, such as walls, metallic objects, or other electronic devices, which can interfere with the WiFi signal.
- Internal Adapter Issues (Advanced): In extremely rare cases, the WiFi adapter itself might be malfunctioning, requiring professional repair or replacement.
Router-Side Troubleshooting: When the Problem's Not in Your Laptop
If the above steps prove unsuccessful, the problem could involve your router or your internet service provider (ISP). To address router-related issues:
1. Router Reboot: The First Line of Defense
Rebooting your router is a foundational troubleshooting step. Unplug your router from its power source. Wait for at least 30 seconds before plugging it back in. Allow the router to fully power up and reconnect to the internet (this can take several minutes).
2. Router Firmware Update: Security and Stability
Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that improve performance, security, and compatibility. Check your router's documentation or the manufacturer's website for instructions on how to update its firmware. This process often involves logging into the router's administrative interface (usually through a web browser by typing the router's IP address – typically 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 – into the address bar).
3. Router Channel Interference: Optimizing for Clarity
WiFi routers broadcast on specific channels. In crowded environments (e.g., apartment buildings, busy neighborhoods), these channels can overlap, causing interference. Access your router's settings to configure the WiFi channel. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are often recommended for 2.4 GHz networks) to find the one that provides the best signal strength. Consider using a WiFi analyzer app (available for both smartphones and computers) to identify less-congested channels in your area.
4. Router Reset (Last Resort): Returning to Factory Settings
If all other troubleshooting steps fail, you might consider resetting your router to its factory default settings. This will erase your custom settings (including your network name and password) and require you to reconfigure the router. This process is performed using a small reset button on the back of the router. Consult your router's manual for detailed instructions.
ISP Issues: When the Problem Lies Beyond Your Control
If you've exhausted all the above steps, and still no WiFi connection, the problem might originate on the ISP's side. Check your ISP's website for service outages in your area or directly contact the ISP's customer support to report the issue.
Advanced Troubleshooting: Beyond the Basics
Once you've tried the steps above, you may need to use other methods:
- Check for Conflicts with Security Software: Occasionally, firewalls or antivirus software might interfere with WiFi connections. Temporarily disable your security software to test this. If the WiFi connects after disabling the software, you'll need to adjust its settings to allow your laptop to connect.
- Network Adapter Reset (Windows): Open Command Prompt as an administrator (search
