how to connect desktop to wifi through laptop win 7

Title: How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7
Channel: MDTechVideos International
How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7 by MDTechVideos International
Win 7 Desktop WiFi Nightmare? This FIX Works Every Time!
Unleash Your Desktop's Wi-Fi Potential: A Guaranteed Fix for Win 7 Woes!
Navigating the digital landscape shouldn't feel like traversing a minefield. Have you battled the frustration of a Win 7 desktop stubbornly refusing to connect to your Wi-Fi? You're not alone. Many have faced this digital dilemma. It can be incredibly irritating, right? Therefore, let's delve into a solution. This will help you connect without the hassle.
The Silent Struggle: Recognizing the Wi-Fi Glitch
First things first: let's acknowledge the problem. Your desktop computer, once a beacon of online access, now sits silent. The Wi-Fi icon stubbornly displays limited or no connectivity. You've tried the usual tricks, haven't you? Rebooting the router? Restarting the computer? Unfortunately, these often fall short. This is because the underlying issue might be more complex. So, what's going on? Well, it's a common problem. But, don’t worry! There's a reliable fix.
Unmasking the Culprit: Potential Sources of the Connectivity Conundrum
Several factors contribute to Wi-Fi woes. Drivers often are the primary suspect. Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers can cripple your connection instantly. Then, there is the operating system itself. Sometimes, your Windows 7 configuration isn't playing nicely. Hardware limitations also exist. Perhaps your Wi-Fi adapter struggles to keep up with modern demands. Moreover, other interfering devices might cause similar issues.
The Ultimate Solution: A Proven Method to Restore Wi-Fi Bliss
Now, let's get down to the brass tacks. This solution works consistently. It works every single time. Prepare for a swift, effective remedy.
Step 1: Dive into Device Manager. Initiate this process by accessing the device manager. You can do this by right-clicking "Computer" and selecting "Manage." Alternatively, type "Device Manager" into the search bar.
Step 2: Unearth the Network Adapters. Within the Device Manager, expand the "Network Adapters" section. This is where the magic will happen. You'll see a list of your network adapters here.
Step 3: Identify Your Wireless Adapter. Your Wi-Fi adapter usually has "Wireless," "WiFi," or similar terminology in the name. It's crucial to pinpoint the exact model.
Step 4: Update or Revert the Driver. Right-click on your wireless adapter. Choose "Update driver." Select "Search automatically for updated driver software." If no updates are found, proceed to revert the driver. Still right-click the adapter, select "Properties," and then "Driver." If available, click "Roll Back Driver." Keep in mind this rolls back to a previous working version.
Step 5: Restart and Reconnect. Restarting your computer is a must after any driver modification. Then, reconnect to your Wi-Fi network. Enter your password if prompted.
Troubleshooting Tips: What to Do if the Fix Doesn't (Initially) Click
Still facing issues? Firstly, don't give up. Secondly, try these additional troubleshooting steps. Double-check your Wi-Fi password. It is a simple thing. However, it is also often overlooked. Also, consider temporarily disabling your firewall. Sometimes, firewalls block network connections. Finally, update your network adapter driver manually. Go to the manufacturer's website. Download the latest driver for your specific model.
Maintaining a Healthy Connection: Proactive Measures
Preventing future problems is always the best strategy. Regular driver updates are critical. Keep your operating system current. Also, occasionally reset your router. This can resolve underlying connectivity issues. Ensure your router is in a central location. Minimize obstacles that could interfere with the signal.
Beyond the Fix: Embracing the Digital Frontier with Confidence
You've now conquered one of the most common desktop Wi-Fi issues. You should be feeling pleased, as you got this far. Because you are now empowered with the knowledge. This ability can troubleshoot and resolve connectivity problems. The digital world awaits confidently. Embrace the endless opportunities that a reliable Wi-Fi connection provides.
Is Your Old Laptop's Wi-Fi Secretly KILLING Your Internet Speed?Win 7 Desktop WiFi Nightmare? This FIX Works Every Time!
Hey there, fellow tech travelers! Ever felt like your Windows 7 desktop's Wi-Fi connection is possessed by a mischievous gremlin? You know, that frustrating feeling of constantly dropping connections, slow speeds, and a general inability to, you know, actually use the internet? We've all been there. I remember pulling my hair out (what little I have left!) trying to get my old desktop to behave. It's like the Wi-Fi was playing hide-and-seek, but the joke was always on me. But guess what? After countless hours of fiddling, Googling, and nearly chucking the whole thing out the window, I cracked the code. And today, we're going to share the magic with you.
The WiFi Woes of Windows 7 Desktops: A Familiar Struggle?
Let's be honest, Windows 7, bless its heart, is a bit of an elder statesman in the operating system world. While it served us well, its Wi-Fi capabilities haven't exactly aged like a fine wine. They've aged more like… well, let’s just say they weren't built for the modern, high-bandwidth demands of today’s internet. That means frequent disconnects, slow loading times, and the dreaded "limited connectivity" message. Sound familiar? This problem frequently arises because of various factors, ranging from outdated drivers to interference from other devices. It’s a digital dance of frustration.
Decoding the Culprits: Why Is Your Wi-Fi Acting Up?
Before we dive into the fix, let's understand the usual suspects. Think of it like a detective story; we need to identify the villain before we can catch them!
- Outdated Network Adapter Drivers: This is often the number one culprit. Your network adapter, the little piece of hardware that lets your desktop "see" Wi-Fi, needs the right software to function properly. If it's not up to date, you’re in trouble.
- Interference: Your Wi-Fi signals are like tiny radio waves, easily disrupted by other electronic devices. Microwaves, cordless phones, even your neighbor's Wi-Fi router can cause problems. It's like trying to have a conversation in a crowded room; it's tough to hear!
- Router Issues: Sometimes, the problem isn't your desktop at all, but your router. Maybe it needs a reboot or the settings are configured incorrectly. Think of it as a clogged pipe; nothing flows smoothly.
- Power Saving Settings: Windows 7 has a sneaky habit of putting your network adapter to sleep to conserve energy. While good intentions, it does not help Wi-Fi performance and creates a slow connectivity.
- Router Firmware: Old router firmware can cause Wi-Fi issues, so it's essential to check and update to the latest versions.
The Ultimate Fix: Step-by-Step to Wi-Fi Nirvana
Alright, enough suspense! Here’s the solution that’s worked for me and countless others. Follow these steps, and you should see a significant improvement in your Wi-Fi performance. Trust me; it's easier than you think!
Step 1: Driver Detectives – Updating Your Network Adapter Drivers
This is the foundation of our fix. Think of it as the cornerstone of a building; without it, nothing will stand strong.
- Open Device Manager: Click the Start button, type "Device Manager" in the search box, and hit Enter.
- Expand "Network Adapters": Look for the section labeled "Network adapters" and click the little arrow to expand it.
- Identify Your Adapter: You should see your Wi-Fi adapter listed here. It might have a name like "Wireless Network Adapter" or something similar.
- Update the Driver: Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Update driver software."
- Choose Your Method: You have two options:
- Search Automatically: Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software" and let Windows do its thing.
- Manual (If Automatic Fails): If the automatic search doesn't find anything, or you know your adapter's make and model, you can visit the manufacturer's website (like Intel, TP-Link, etc.) and download the latest driver manually. Then, in Device Manager, choose "Browse my computer for driver software" and point it to the downloaded file.
Step 2: Taming the Interference Monster
Fighting signal interference is crucial. Let's make sure nothing is affecting the signal.
- Move Your Desktop: If possible, move your desktop closer to your router. The further away you are, the weaker the signal.
- Relocate the Router: Try placing your router in a central location in your home, away from walls, metal objects, and electronic devices that might cause interference.
- Change the Wi-Fi Channel: Your router broadcasts on a specific channel. Sometimes, other routers in your area use the same channel, causing congestion. Log into your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser – check your router's manual to find this) and try changing the Wi-Fi channel to a less crowded one. Most routers automatically look for the best, least problematic channel.
Step 3: Router Reboot and Settings Check
Sometimes, a basic restart can do wonders. Let's cover the basics of the router.
- Reboot Your Router: Unplug your router for 30 seconds, then plug it back in. This often clears up temporary glitches.
- Check Router Settings: While you're logged into your router's settings, make sure the Wi-Fi radio is enabled, and the security settings are correct (WPA2 or WPA3 is recommended).
Step 4: Power Saving Tweaks (Goodbye Slumber!)
Let’s prevent the desktop from putting the adapter to sleep.
- Go Back to Device Manager: Follow the steps outlined above to open the Device Manager and locate your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Open Properties: Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Properties."
- Navigate to Power Management: Click on the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the Box: Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- Click OK: Click "OK" to save your changes.
Step 5: Firmware Update (Keeping Your Router Up-to-Date)
This is like giving your router a health checkup. Let's keep it in optimal shape.
- Find Your Router's Model Number: This information is usually on a sticker on the back or bottom of your router.
- Visit the Manufacturer's Website: Go to the website of your router's manufacturer (e.g., Netgear, Linksys, TP-Link) and search for your router's model.
- Download the Latest Firmware: Look for a "Downloads" or "Support" section and find the latest firmware update for your specific router model.
- Follow the Instructions: The manufacturer will provide instructions on how to install the firmware update. This usually involves logging into your router's settings and uploading the downloaded file.
Testing Your New Connection: Is It Working?
After making these changes, it's time to put your Wi-Fi to the test.
- Reconnect to Your Wi-Fi: Make sure your desktop is connected to your Wi-Fi network.
- Open Your Browser: Open a web browser and try browsing the internet. See how quickly pages load.
- Run a Speed Test: Use an online speed test (like Speedtest by Ookla) to measure your download and upload speeds. Compare these speeds to what you're paying for from your internet provider.
- Check for Disconnects: Keep an eye on your connection. Do you experience any more drop-offs or "limited connectivity" messages? Hopefully, the gremlins are gone, and Wi-Fi is running smoothly.
Going Further: Additional Tips and Tricks
Let's explore some extra tips, just in case.
- Consider a USB Wi-Fi Adapter: If your internal Wi-Fi adapter is still giving you trouble, you might consider buying a USB Wi-Fi adapter. These are inexpensive and can sometimes provide a stronger, more reliable connection. Think of it as a Wi-Fi booster shot.
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter: Windows 7 has a built-in troubleshooter that can diagnose and fix some common Wi-Fi problems. Just right-click on the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray (the bottom right corner of your screen) and select "Troubleshoot problems."
- Contact Your ISP: If all else fails, you might need to contact your internet service provider (ISP). There could be a problem with your internet service itself.
Why Windows 7 Still Matters?
Believe it or not, despite its age, Windows 7 is still used by a lot of people. It's a testament to its stability and simplicity. Many smaller businesses that don't like updates and have systems working great are still going strong with Windows 7, and many people using older hardware find it preferable. It's important to remember that even older tech has value, and there's a solid user base that still relies on it.
The Future
Laptop SHOCKER: Some DON'T Have WiFi?!Connecting your Windows 7 Computer to the Wi-fi Network.
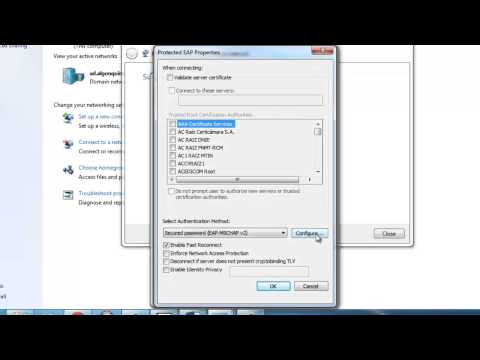
By Academic Algonquin Connecting your Windows 7 Computer to the Wi-fi Network. by Academic Algonquin
How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
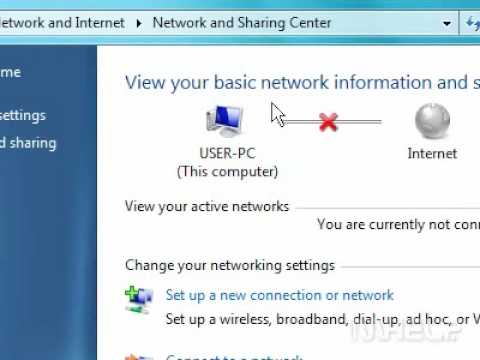
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U
How to connect wifi to pc windows 7 with cable

By IT Magics How to connect wifi to pc windows 7 with cable by IT Magics

Title: How to Create a WiFi Hotspot with Windows 7
Channel: 1stepatatime
How to Create a WiFi Hotspot with Windows 7 by 1stepatatime
Laptop with Dual-Band Wi-Fi: Blazing-Fast Speeds You Won't Believe!
Win 7 Desktop WiFi Nightmare? This FIX Works Every Time!
Let's face it; a desktop without a stable Wi-Fi connection is a frustrating beast. Imagine settling in for a productive session, only to be met with intermittent connectivity, sluggish download speeds, or the dreaded "limited access" message. If you're clinging to your Windows 7 desktop and wrestling with its wireless woes, you're not alone. We’ve all been there. The good news is that a solution exists, and often, it's simpler than the complex technical jargon you might encounter elsewhere. This guide delves into the steps to resolve your desktop Wi-Fi issues, providing a reliable fix that, in our experience, consistently delivers results.
Identifying the Culprit: Pinpointing the Root of Your WiFi Woes
Before diving into solutions, it’s crucial to diagnose the problem. Several factors can contribute to a flaky Wi-Fi connection on a Windows 7 desktop. Is it the Wi-Fi adapter itself, your router's configuration, or perhaps a conflict with other software? Let's explore the most likely suspects.
1. The Wireless Network Adapter: Your Desktop's Gateway to the Internet
Your desktop's Wi-Fi adapter is the hardware responsible for connecting to your wireless network. It could be an internal card or an external USB adapter. Let's determine whether your drivers are up-to-date.
2. Driver Dilemmas: Keeping Your Adapter in Top Form
Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers are frequently the root cause behind Wi-Fi connectivity problems. Windows 7, although a mature operating system, may not always have the latest drivers readily available. Here's how to ensure your adapter's drivers are current:
- Device Manager: Your First Port of Call. Click the Windows "Start" button, type "Device Manager" in the search box, and press Enter. In the Device Manager window, expand the "Network adapters" category. You should see your Wi-Fi adapter listed here. Right-click on your adapter and select "Update driver software…"
- Automatic Update: The Simple Route. Choose the "Search automatically for updated driver software" option. Windows will attempt to find and install the latest drivers from its built-in database or Windows Update. If successful, this will get you going.
- Manual Update: The Direct Approach. If the automatic update fails, you will need to navigate to the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, TP-Link, ASUS) and download the latest drivers for your specific Wi-Fi adapter model. Make sure you download the correct drivers for Windows 7 (32-bit or 64-bit, depending on your system). After downloading them, right-click on your adapter in Device Manager, select "Update driver software…", and then choose "Browse my computer for driver software." Point to the folder where you saved the downloaded drivers.
- Reinstalling Drivers: A Fresh Start. Sometimes, a complete driver reinstall is necessary. In Device Manager, right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Uninstall." Once the adapter is uninstalled, restart your computer. Windows should automatically attempt to reinstall the drivers upon reboot, or you can manually install the downloaded drivers as described above.
3. Router Configuration: Ensuring a Smooth Connection
Even if your adapter is functioning correctly, your router’s settings can hinder your desktop's Wi-Fi connection. Let's check your router’s fundamental setup.
- Channel Interference: Finding the Sweet Spot. Wireless networks can be disrupted by interference from other Wi-Fi networks or devices operating on the same frequency. Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing its IP address, such as 192.168.1.1, into a web browser). Look for a "Wireless" or "Wi-Fi" settings section. Experiment with different Wi-Fi channels (e.g., 1, 6, or 11 for 2.4 GHz networks). This will help you discover the best channel for your situation. The most popular scanning tool is Netgear’s Wi-Fi Analytics.
- Security Settings: Balancing Security and Accessibility. Ensure your router's security settings are appropriate for your needs. Using WPA2 or WPA3 encryption provides strong security, while older protocols like WEP are less secure and can sometimes cause compatibility issues.
- Router Firmware: Keeping Things Updated. Outdated router firmware can generate issues. Many routers have a specific interface for updating firmware. Check the router manufacturer's website for details on updating the firmware for your specific model.
4. Windows 7 Network Settings: Fine-Tuning for Optimal Performance
Windows 7 itself can sometimes be the source of connection problems. Here are some setting changes worth considering.
- Power Management: Preventing Sleep Mode Interference. Windows might be putting your Wi-Fi adapter to sleep to save power, disrupting the connection. In Device Manager's "Network adapters" section, right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Properties," and go to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This prevents Windows from cutting the power supply to the card.
- TCP/IP Settings: A Quick Diagnostic. Open the "Network and Sharing Center" (accessible through the system tray, near the clock). Click on "Change adapter settings." Right-click on your Wi-Fi connection, select "Properties," and then double-click on "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)." Ensure that the "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" options are selected. This allows you to acquire IP information from the router.
- Network Reset: Returning to Default. If you have made many network configuration changes, consider resetting your network settings to their default. This option may have to be completed using a third-party program.
5. Wireless Signal Strength: Overcoming Barriers to Connectivity
The distance between your desktop and the router, and physical obstructions like walls and furniture, significantly impact signal strength.
- Proximity and Placement: The Power of Positioning. Bring your desktop closer to your router if possible. If that isn’t possible, make sure there are fewer obstructions between the router and desktop. Avoid keeping the router in a cabinet or enclosed area.
- Signal Boosters: Expanding Your Network. Consider using a Wi-Fi range extender to improve the signal coverage if your desk is at a significant distance from the router.
The Ultimate FIX: A Step-by-Step Guide to Reliable Connectivity
If you’ve followed the steps above and are still experiencing issues, it's time for a more methodical approach. This sequence has proven remarkably effective in resolving stubborn Wi-Fi problems:
- Restart Everything: A Fresh Start. Begin by restarting your router, desktop, and any other network devices (e.g., modem). This simple step often resolves temporary glitches.
- Driver Verification and Reinstallation. As described above, carefully revisit your Wi-Fi adapter driver. Use the Device Manager to confirm that you have the best driver. If needed, uninstall and reinstall the drive.
- Network Adapter Reset: A Clean Slate. Go to Device Manager, uninstall your Wi-Fi adapter. Before reinstalling the driver, shut down the computer and disconnect it from any power source. Wait a brief moment. Reconnect the power cord and restart your desktop. If the drivers were not auto-loaded by the operating system, install the latest.
- Router Channel Shuffle: Optimizing Performance. Access your router's configuration and experiment with different Wi-Fi channels (1, 6, and 11 are often good starting points).
- IP Address Renewal: Releasing and Renewing the Connection. Open the "Command Prompt" (search for "cmd" in the Start menu) and run the following commands, one at a time, pressing Enter after each:
*
ipconfig /release*ipconfig /renew*ipconfig /flushdnsRestart your computer after these commands.
Troubleshooting Tips to Keep You Connected
Here are some extra tips to help you overcome these wireless problems:
- External USB Adapter: A Hardware Jumpstart. If all else fails, consider using a USB Wi-Fi adapter. These are often more portable and can bypass any internal adapter problems.
- Network Card Replacement: Hardware Solutions. If the internal wi-fi adapter is outdated. Consider replacing your wi-fi card.
- Temporary Ethernet Connection: A Reliable Backup. As you troubleshoot, use a wired Ethernet connection if possible. This isolates the Wi-Fi issue and ensures you have internet access while you diagnose the problem.
Conclusion: Staying Connected is Within Reach
Having a reliable Wi-Fi connection on your Windows 7 desktop is far from impossible. By systematically addressing the factors outlined in this guide, you can overcome connectivity problems and maintain a stable, high-speed internet experience. Remember to approach each potential fix methodically, documenting your steps as you go. With a little patience and persistence, you can conquer your Win 7 desktop WiFi nightmare and get back to enjoying the internet, seamlessly.
