how to connect windows xp laptop to wifi
Title: How to connect Windows XP to your wireless network
Channel: NetComm
How to connect Windows XP to your wireless network by NetComm
how to connect windows xp laptop to wifi, can windows xp connect to wifi
Unlock Your XP Laptop's WiFi: The Secret Guide!
Unleash the Wireless Wonders: Your XP Laptop's Ultimate WiFi Revival!
Remember those days? The clunky charm of your Windows XP laptop. It was a technological cornerstone. But, did your WiFi connection feel less like a superhighway and more like a forgotten dirt road? You are not alone. Many users struggled. Getting that vintage machine online can feel like an archaeological dig. The process, though, doesn't need to be daunting. Instead, think of this as a treasure hunt.
Decoding the WiFi Puzzle: Initial Diagnosis
Before you start, take a deep breath. Don't let frustration cloud your judgment. First, let's clarify what's happening. Is your WiFi icon showing a big red "X"? That's a sign. Is it showing a limited connection? That's also a clue. Because of this, you need to investigate. Start by checking the physical switch on your laptop. Some XP machines have a physical WiFi button. Is it flipped on? Next, examine your network adapter settings. Furthermore, right-click the "My Computer" icon. Select "Manage". Then, click on "Device Manager". Expand "Network adapters." If you see a yellow exclamation mark, you have an issue.
The Driver Dilemma: Your First Hurdle
Drivers are the lifeblood of your WiFi connection. Without them, your laptop is blind. They are essential. Often, outdated or corrupted drivers are the culprit. So, let's fix this. First, identify your network adapter. This information is available in the Device Manager. After that, you will need to find the correct driver. Consider the manufacturer's website. They usually have downloads for older hardware. Go to the manufacturer's website. Then, search for your model. Download the relevant driver. It should be for Windows XP. Now, install the driver following the on-screen prompts. After the installation, reboot your laptop. Because of this, your WiFi may spring back to life.
Unveiling Hidden Networks: SSID Secrets
Is your network visible? Sometimes, your router might be hidden. So, let's check. Look for the SSID, your network name. If your network is hidden, you must manually add it. Go to your WiFi settings. Select "View available wireless networks." Choose "Change the order of preferred networks." Click "Add". Enter your network's SSID. Also, enter the security key. Save your settings. After you save it, try connecting again.
Security Protocols: WEP, WPA, and the Wireless World
WiFi security has evolved. XP laptops might struggle with modern protocols. Older routers sometimes use WEP. This is less secure. WPA and WPA2 are usually better. Therefore, ensure compatibility. Check your router's settings. See what security protocols it supports. Try using WPA or WPA2 if possible. Because of this, your connection will be more secure. Consider changing your router settings if needed. Also, make sure your laptop's security settings match your router’s.
Troubleshooting Tactics: When Things Get Tricky
Still no luck? Don't give up. Let's try some more tactics. Firstly, restart your router. Power cycling can work wonders. Unplug it for 30 seconds. Plug it back in. Secondly, consider your firewall. A firewall might block your connection. Temporarily disable your firewall. Then, try connecting again. If that works, configure the firewall. Allow your WiFi adapter access. Thirdly, check your IP address settings. Ensure you're obtaining an IP address automatically. You can also try a static IP, if needed. Finally, consider the distance. Are you far from your router? Move closer.
The Power of Persistence: Success is Within Reach
Dealing with older technology can be challenging. However, it's often rewarding. Because you are here indicates you are taking initiative. Keep trying different solutions. Search online forums. Read user guides. The community is vast. Moreover, if you've tried everything, and still fail, don't hesitate to seek professional help. Local computer repair shops can assist. Therefore, stay patient. Success with your XP laptop's WiFi is within reach. You just need the right approach.
Beyond Connection: Enhancing Your XP Experience
Once your WiFi is working, consider further upgrades. A faster connection unlocks more possibilities. Explore lightweight browsers. They are optimized for older hardware. Also, consider security software. Furthermore, keep your operating system updated. Consequently, this ensures better security. Remember, your XP laptop still has value. Now, enjoy the internet!
Steal Your Laptop's WiFi: Secret Phone Trick Revealed!Unlock Your XP Laptop's WiFi: The Secret Guide!
Ah, Windows XP. A relic of a simpler time, isn't it? Remember that feeling of pure digital freedom? Well, maybe not pure freedom, especially when you're staring at a blank WiFi icon on your trusty XP laptop. Getting that old machine online can feel like cracking a cryptic code, but fear not, fellow tech travelers! We’re here to decrypt that WiFi puzzle and get you connected. Consider this your secret map to wireless bliss.
1. The Nostalgic Labyrinth: Why Bother With XP WiFi Anyway?
Before we dive headfirst into the technical weeds, let's address the elephant in the room (or, in this case, the vintage laptop on your desk): why even bother getting WiFi working on an XP machine in the modern age? Well, besides the sheer thrill of resurrecting legacy technology, there are a few legitimate reasons. Maybe you’re a retro-gaming enthusiast, and you want to experience online multiplayer in all its pixelated glory. Perhaps you’re a collector, wanting to preserve and access files on your old system. Or maybe, just maybe, you're like me – someone who appreciates the charm and simplicity of a bygone era. Plus, let's be honest, there's a certain satisfaction in proving to the world that you can still make XP work, even when faced with modern security protocols. It’s like saying, "Yeah, I can still drive a manual transmission!"
2. Spotting the WiFi Signal: Is Your XP Laptop Ready?
First things first, let's make sure your XP laptop even has the necessary hardware for wireless connectivity. Think of it like checking your car for an engine before you plan a road trip. Most laptops built during the XP era came equipped with some form of WiFi capabilities.
- Check the Physical Switch: Many laptops had a physical switch (often on the side or front) that toggled the wireless adapter. Make sure it’s switched on. This is the most common oversight, trust me! I learned this the hard way, spending hours troubleshooting a "dead" WiFi card only to realize the switch was off.
- The WiFi Icon: Look for a small, curved antenna icon in your system tray (usually near the clock). If it’s there and showing a red "X," then you're likely facing a connectivity issue rather than a hardware problem.
- Device Manager Deep Dive: If the icon is MIA, it’s time to dig a little deeper. Click "Start," then "Control Panel," then "System," and finally "Hardware." Click the "Device Manager" button. Expand the "Network adapters" section. Do you see your wireless network adapter listed without any exclamation marks or errors? If so, your hardware is likely recognized. If not, you might have a driver issue, which we’ll address later.
3. Decoding the Drivers: The Key to the Wireless Kingdom
Drivers are like the translators that allow your Windows XP machine to speak the same language as your WiFi adapter. Without the right drivers, your laptop is essentially mute. If you suspect driver issues, here’s what to do:
- Identify Your Adapter: Go back to Device Manager (as described above). Note the name of your wireless network adapter. It might be something like "Intel PRO/Wireless 2200BG Network Connection" or "Broadcom 802.11g Network Adapter."
- The Driver Hunt: Head to the internet (on another device, of course!) and search for the drivers for your specific adapter model, and importantly, specifically for Windows XP. This is crucial. Newer drivers simply won't work. Manufacturer websites (Intel, Broadcom, etc.) are usually the best place to start.
- Installation Adventure: Download the driver, and then double-click the downloaded file to initiate the installation. Follow the on-screen instructions. Sometimes, you might need to manually point Windows to the driver files within Device Manager (Right click on your adapter in Device Manager, choose "Update Driver," then search for the extracted driver files).
4. The Security Siren (and How to Outsmart Her): WEP, WPA, and WPA2
Here's where things get a little tricky. Modern WiFi routers use security protocols that XP wasn’t originally designed to handle easily. The goal is to keep your data safe. When you try to connect to your home WiFi, you have to authenticate with a password.
- The WEP Warning: Older routers might use WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), a security protocol considered quite vulnerable today. If your router is set to WEP, your XP machine might connect easily, but at a significant security risk. It's like leaving your front door unlocked.
- The WPA/WPA2 Challenge: More secure protocols like WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2 are the norm now. XP support for these protocols can be spotty. You may need to download security updates from Microsoft or use third-party software solutions. We'll cover some of these solutions in the next section.
- The Easy Route (If Possible): If you have control over your router, the easiest solution might be to temporarily configure it for WPA/WPA2 and a compatible security setting, such as TKIP + AES encryption (though it’s not ideal for long-term security). This often works for initial connection purposes.
5. Patching the Past: Security Updates and Third-Party Saviors
Sometimes, the official Microsoft updates are your salvation. Other times, you may need to enlist the help of some third-party programs to get WiFi to run.
- Microsoft’s Final Stand (Updates): Although Microsoft officially ended support for XP in 2014, some updates might be available that address WPA/WPA2 compatibility issues. Google "Windows XP WPA2 update" and see if you can find anything helpful. However, I would be cautious about installing these updates, as many were designed to secure your system with the current level of technology.
- The Wireless Configuration Wizard: Right-click on the WiFi icon in your system tray. Do you see the option to “View Available Wireless Networks”? If so, this is a good sign, and you can walk through the steps to identify your wireless network and enter the password.
- Third-Party Heroes (Wireless Software): Consider using third-party wireless configuration software. These tools often have better support for modern security protocols. Search online for "XP wireless configuration software" or "XP WiFi manager." They may help you connect to modern networks.
6. The Hidden SSID Gambit: Finding a Secret Network
Your router might be set to "hide" its network name (SSID), making it invisible to your XP machine at first. This is a security measure, though not a particularly strong one.
- Know Your SSID: Beforehand, find out your network's SSID from your router's settings or another device connected to your network.
- Manual Configuration: In Windows XP's wireless connection settings, you should have the option to manually add a network. Enter the SSID, select the appropriate security type (WPA/WPA2), and enter your password.
- Persistence Pays: Sometimes, it takes a few tries. Double-check your password and the security settings on your router.
7. MAC Address Maneuvers: Allowing Access
Your router can filter devices based on their MAC addresses, a unique identifier for each network adapter. If your XP laptop's MAC address isn't whitelisted, it won't be allowed to connect.
- Find Your MAC Address: Open a Command Prompt (Start -> Run -> type "cmd" and press Enter). Type "ipconfig /all" and press Enter. Look for "Physical Address," which is your MAC address.
- Router Configuration: Log into your router's interface (usually through your web browser). Find the MAC address filtering section and add your XP laptop's MAC address to the allow list.
8. The IP Address Assignment: Static vs. Dynamic
Your XP laptop needs an IP address to communicate on the network.
- Dynamic IP (DHCP): Most routers assign IP addresses automatically (DHCP). This is usually the easiest option. Ensure your XP laptop is set to obtain an IP address automatically.
- Static IP Adventure: If you're having connection problems, you can try assigning a static IP address. This involves manually assigning an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers. This can be tricky, so only attempt this if you understand the basics of networking. Be careful with this one; a wrong setting can cause a lot of trouble.
9. Firewall Frenzy: Taming the Digital Beasts
Your Windows firewall might be blocking your internet connection. It’s like a gatekeeper that might mistakenly deny your access to the outside world.
- Temporarily Disable the Firewall: As a test, temporarily disable the Windows Firewall (Start -> Control Panel -> Windows Firewall). Try connecting to the internet again. If it works, the firewall was indeed the culprit.
- Configure the Firewall: If the firewall was the issue, you can configure it to allow internet access for applications that need it. This usually involves adding the application or port to the firewall's exceptions list.
10. The DNS Dip: Solving the Domain Name Mystery
DNS (Domain Name System) servers translate website addresses (like google.com) into IP addresses. Issues with DNS
WiFi Dead? Get It Back ON Your Laptop NOW!How to connect wireless wifi to windows XP Very Simple.
By NAjam UL HAssan How to connect wireless wifi to windows XP Very Simple. by NAjam UL HAssan
How to Connect to the Internet in Windows XP PC

By How-To Guide How to Connect to the Internet in Windows XP PC by How-To Guide

Title: How To Fix Wifi Not Working In Windows XP Tutorial
Channel: MDTechVideos
How To Fix Wifi Not Working In Windows XP Tutorial by MDTechVideos
Laptop Wifi Connect
Unlock Your XP Laptop's WiFi: The Secret Guide!
We've all been there. You've dusted off that trusty old XP laptop, perhaps for a nostalgic trip down memory lane or maybe to run some legacy software. You power it up, ready to connect to the world, and… no WiFi. Panic starts to set in. Fear not! We’re here to guide you, step-by-step, through the often-intricate process of getting your Windows XP laptop connected to the internet via WiFi. Forget those frustrating forum threads and outdated tutorials. We’re offering the definitive guide to conquering your connectivity woes.
Understanding the WiFi Landscape on Windows XP
Before we dive into solutions, it's crucial to understand the limitations and quirks of WiFi on Windows XP. This operating system, despite its age, can still reliably connect to modern networks, provided you navigate the potential pitfalls. Key factors to consider are your laptop's wireless card, the security protocols used by your router, and the specific configuration settings within XP itself. We’ll address each of these to ensure a successful connection.
Verifying Your Wireless Network Adapter's Presence and Functionality
The first step is to ascertain whether your laptop even has a wireless network adapter and, crucially, if it's functioning correctly. This seemingly simple step trips up many users.
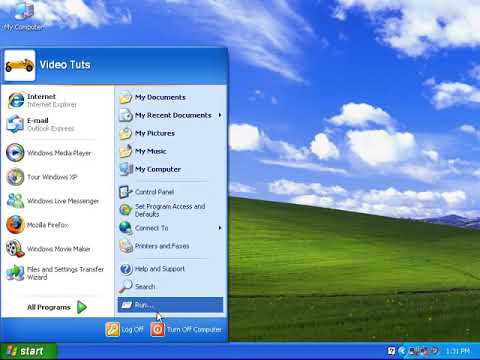
Accessing Device Manager: Click the "Start" button, then right-click "My Computer" and select "Manage." This opens the Computer Management window. In the left-hand pane, click "Device Manager."
Locating the Network Adapters: Expand the "Network adapters" section. You should see a list of installed network devices. Look for an entry that includes terms like "Wireless Network Adapter," "802.11," or something similar indicating it's a WiFi device.
Interpreting the Icons:
- No Icon: If you don’t see a wireless adapter listed at all, then either your wireless card is not installed, disabled in the BIOS, or has a hardware failure. Check your laptop manufacturer's documentation on how to re-enable it or if there is a hardware failure.
- A Yellow Exclamation Mark (!): This indicates a driver problem. The wireless adapter is present but not functioning correctly. Proceed to steps 4.
- A Red "X": This shows the adapter is disabled. You may be able to re-enable it by right-clicking on the adapter and selecting "Enable."
- No issues: If your wireless adapter is listed without any special icons, that's a great sign!
Updating or Reinstalling Drivers (if needed): If you have the yellow exclamation mark, double-click on the wireless adapter entry. In the Properties window, go to the "Driver" tab. Click "Update Driver." You can then choose to search automatically for updated drivers, or if you have a driver file available, navigate to it manually. The best method will be to download them from the product's website. If you're having trouble finding the right drivers, you may need to go to download drivers on another computer.
Re-enabling the Adapter (if disabled): If you disabled the adapter in the Device Manager, right-click it and select "Enable." If you continue to have issues, you may need to contact your product's manufacturer.
Configuring the Wireless Network Connection in Windows XP
Assuming the wireless adapter is present and functioning, the next step is to establish a connection to your WiFi network. This involves configuring your wireless network settings within Windows XP. This configuration needs to be completed correctly to achieve a successful connection.
Open Network Connections: There are several ways to access this panel. The quickest is to go to start -> Control Panel -> Network Connections.
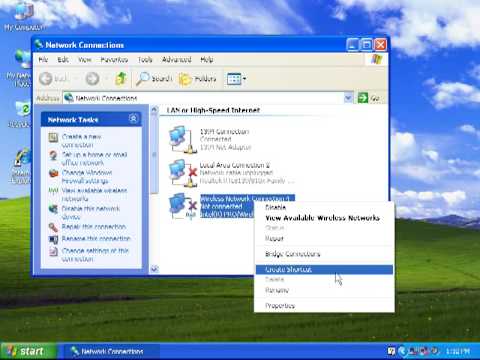
Finding Available Networks: In the Network Connections window, right-click on the "Wireless Network Connection" (it might have a different name depending on your hardware). Select "View Available Wireless Networks."
Selecting Your Network: A list of available WiFi networks will appear. Select your network from the list. If your network requires a password, you will be prompted to enter it. Enter it correctly.
Security Protocol Verification: The most common security protocols are WEP, WPA, and WPA2 (or WPA3). Windows XP natively supports WEP and WPA (though WPA support may require a service pack update). WPA2 is more secure but may require some extra effort. If your router is configured for WPA2, and your Windows XP system does not have the right drivers, the connection may not work. Consider upgrading your XP to the newest service pack.
Manual Configuration (if necessary): If your network is hidden or Windows XP doesn't automatically detect it, you'll need to manually configure the connection:
- In the Network Connections window, right-click on "Wireless Network Connection" and select "Properties."
- In the "Wireless Networks" tab, click "Add."
- Enter your network's SSID (the name of your network).
- Select the Security type (WEP, WPA, or WPA2). If connecting to a newer WPA2-encrypted network, ensure your encryption type matches your router's settings. Make sure you have the right security key available.
- Enter the network key (password).
- Ensure "This is a computer-to-computer (ad-hoc) network; wireless access points are not used" is unchecked unless you are creating an ad-hoc network.
Obtaining an IP Address: Once connected, your laptop needs an IP address to communicate on the network. Make sure your WiFi network is set to obtain the IP address or get configuration automatically.
If your router uses DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, the most common setup), your laptop should automatically acquire an IP address and DNS settings. Check in your connection's properties to confirm that its configuration is set to get an IP address automatically.
If you need to set a static IP address, the connection will fail automatically. Go to its properties, double-click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
- Select “Use the following IP address”
- IP Address: Enter the IP address for your computer. It should be within the same range as your router's IP address. (e.g. 192.168.1.X, where X ranges from 2 to 254). Check your Router's manual for documentation.
- Subnet mask : Usually 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway: Your router's IP address.
- Preferred DNS Server: You your ISP's DNS server, or a public DNS from, for example, Google (8.8.8.8).
- Alternate DNS server: Another DNS from your ISP, or Google's (8.8.4.4)
Troubleshooting Connection Issues: If you're still not connected, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Restart: Restart your computer and the router.
- Firewall: Temporarily disable your firewall to see if it's blocking the connection.
- Router Compatibility: Make sure your router is not set to something your XP system doesn't support.
- Check Signal Strength: If the signal strength is weak, move your laptop closer to the router or consider using a network extender.
Addressing Security Protocols and Legacy Issues
Windows XP's support for modern security protocols can sometimes be problematic. Let's examine this for a secure connection.
WPA2 or WPA3 Considerations: While Windows XP can connect to WPA2 networks (and in some cases, WPA3, but not natively), you may need to update the drivers for your wireless adapter. In many cases, the older drivers included with Windows XP do not support the most up-to-date security measures. Check your laptop manufacturer's website for updated drivers.
WEP Security: WEP is an older and less secure protocol. If your router is set to WEP, this is inherently less secure. Consider updating it to WPA or WPA2.
Service Pack Implications: Ensure that your Windows XP installation has the latest service pack (ideally, Service Pack 3). Service packs include critical security updates and bug fixes that can improve compatibility with modern hardware and security protocols. Install the product and restart your computer.
Wireless Adapter Firmware: Some wireless adapters have firmware, which could be outdated. Look for firmware updates on the manufacturer's website. Firmware, like drivers, can improve compatibility and performance.
Final Steps for Seamless WiFi on Your XP Laptop
Once you have a stable WiFi connection, here are a few final touches:
- Test Your Internet Connection: Open your web browser and navigate to a website to confirm that you have an internet connection.
- Update Applications: Update your web browser and any other software that requires an internet connection.
- Secure your XP System: Even when using an outdated operating system, you can take special measures to protect your system from cybersecurity risks.
- Install a reputable antivirus software and keep it updated.
- Enable Windows Firewall.
- Be cautious about

