laptop won't connect to wifi windows 7
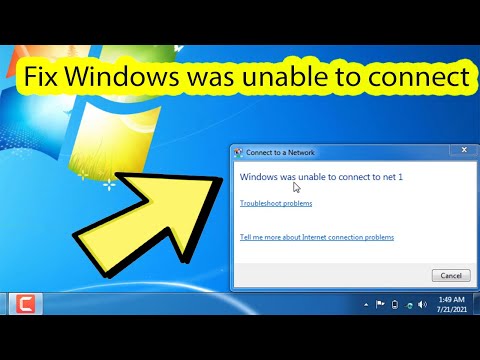
Title: Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop
Channel: IT Magics
Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop by IT Magics
laptop can t connect to wifi windows 7, laptop cannot connect to wifi windows 7, laptop won t connect to wifi windows 7, my laptop cannot connect to wifi windows 7, hp laptop cannot connect to wifi windows 7, my laptop won t connect to wifi windows 7, my toshiba laptop won t connect to wifi windows 7, my hp windows 7 laptop won t connect to wifi, hp laptop windows 7 won t connect to wifi, why is my windows 7 laptop not connecting to wifi
WiFi Nightmare on Windows 7? Fix Your Laptop NOW!
Battling the WiFi Demons: Reclaiming Your Windows 7 Laptop's Connectivity
Ah, the familiar frustration. Your Windows 7 laptop stubbornly refuses to connect. It’s a WiFi nightmare. Don't panic. We've all been there. This guide arms you. It equips you to vanquish these digital gremlins. Let’s get your laptop back online.
Troubleshooting the WiFi Woes: Decoding the Symptoms
First, let's diagnose the problem. Is the WiFi icon showing a red X? Do available networks refuse to appear? Perhaps you are connecting but speeds are glacial. These are the usual suspects. Identify the specific struggle. This will guide your actions. Therefore, let’s explore the most likely culprits.
Network Adapter Mayhem: A Software Showdown
Your network adapter is the key. It's the translator between your laptop and the router. Unfortunately, it's often the source of the problem. First, update the drivers. Visit your laptop manufacturer's website. Search for your model. Download the latest network adapter drivers. Install them carefully. Restart your laptop after the installation.
Driver Dilemma: A Critical First Step
Outdated drivers are a frequent issue. They can cause major connectivity hiccups. Consequently, updating them should usually fix things. If the problems persist, consider a driver rollback. Go to Device Manager. Right-click on your network adapter. Select "Properties". Under the "Driver" tab, you'll find "Roll Back Driver." This reverts to the previous version.
The Router Rumble: Examining the Hardware
Your router is your gateway to the internet. Often, the problem is the router, not your laptop. Begin by restarting your router. Unplug it for a minute. After a minute, plug it back in. Allow it to fully boot up. Then, reconnect your laptop.
Signal Strength Struggles: Navigating WiFi Signals
Poor signal strength is a common complaint. Position your laptop closer to the router. Physical obstructions can weaken the signal. Walls and appliances can interfere. Also, adjust your router's placement. Try elevating it. Make sure there are no obstructions hindering its signal.
Network Settings Nuisances: Checking Configuration
Incorrect network settings can also sabotage your connection. Double-check your network's security key. Ensure that you have the correct password. Verify the network type is appropriate. Try forgetting the network. Then, reconnect to it.
Interference Intrusions: Fighting Wireless Warfare
Other devices cause interference sometimes. Wireless phones and microwaves use the same frequencies. They can interfere with your WiFi signal. Distance can help mitigate this. Also, try changing your router channel. You can do this through your router's settings.
IP Address Investigation: A Digital Detective Story
Sometimes, your IP address is the issue. You might have a static IP address configured incorrectly. Or, there might be conflicts. To resolve this, go to your network adapter settings. Select "Obtain an IP address automatically." Then, select "Obtain DNS server address automatically". Restart your laptop again.
Firewall Frustrations: A Security Checkpoint
Your firewall might be blocking your internet access. This is a security measure. However, it can sometimes hinder your connection. Temporarily disable your firewall. See if this fixes the problem. If it does, adjust its settings. Specifically, unblock the network adapter.
Network Reset Revival: The Ultimate Option
If all else fails, consider a network reset. This restores your network settings to default. However, be warned. This will erase saved WiFi passwords. Open the Network and Sharing Center. Click "Change adapter settings". Right-click on your network adapter. Select "Disable" then "Enable". This can sometimes provide a fresh start.
Seeking Expert Assistance: When to Call for Backup
If complications persist, seek expert help. Consider consulting with a computer technician. They can diagnose complex problems. They possess specialized tools. They will provide professional solutions. Don't let frustration win.
Reclaiming your WiFi connection requires patience. Also, it will need some troubleshooting. However, with these tips, you can usually conquer the WiFi demons. Go forth and conquer your Windows 7 laptop’s persistent connectivity issues. You've got this!
Is Your Laptop Secretly Single-Band? (WiFi Speed SHOCKER!)WiFi Nightmare on Windows 7? Fix Your Laptop NOW!
Let's face it, we've all been there. That moment of sheer frustration when your laptop, a supposed portal to the digital world, decides to stage a silent, screen-frozen protest against your will. And more often than not, the culprit? The dreaded WiFi connection, or rather, its complete and utter absence. If you're still rocking a Windows 7 machine (hey, no judgment, we've all been there!), and you're battling a WiFi gremlin, prepare for a deep dive into the digital trenches. Because, trust me, we've got the battle plan to get you back online, back in the game, and back to binge-watching those cat videos.
1. The Ghosts in the Machine: Recognizing the WiFi Woes
Before we can slay this WiFi dragon, we need to identify its symptoms. Is your WiFi simply not connecting? Are you getting that infuriating "Limited Access" message? Or perhaps, the connection is there, but the speed is slower than a snail crossing a highway? The first step is to recognize the enemy. Think of it like being a detective. We need to gather clues! This could involve troubleshooting by clicking through the network icon in the system tray, going to settings, or, we can even check the device manager.
2. Driver's Seat: Ensuring Your Wireless Adapter is Up to Speed
Imagine your wireless adapter is a race car. Now, even the sleekest, shiniest vehicle won't win a race without a skilled driver, right? Your "driver" in this case is the driver software for your wireless adapter. If this software is outdated, corrupt, or missing, your laptop is basically stuck in neutral.
- How to check your wireless adapter:
- Click on the "Start" button.
- Right-click on "Computer" and select "Manage."
- In the left pane, click on "Device Manager."
- Expand "Network adapters." You should see your wireless adapter listed here (e.g., "Wireless Network Adapter").
- Updating your driver:
- Right-click on your wireless adapter.
- Select "Update Driver Software…"
- Choose "Search automatically for driver software."
- If that doesn't work, try finding the driver on the manufacturer's website, downloading it, and installing it manually. Sometimes a manual install is just what the doctor ordered!
3. The Simple Solutions: Quick Fixes That Sometimes Actually Work!
Before we launch into the heavy artillery, let's try some of the easy stuff. Think of it like checking the fuse box before calling an electrician.
- Restart your laptop: Seriously, it's the IT guy's mantra for a reason. Often, a simple reboot clears up a multitude of sins.
- Restart your router and modem: Unplug them both, wait 30 seconds (or, you know, make a cup of coffee), and plug them back in. This resets the network connection from the source.
- Toggle Wireless on/off: Locate the physical or software switch on your laptop that controls the WiFi, and make sure it's turned on. Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the best.
- Forget and Reconnect: In your network settings, "forget" your WiFi network and then reconnect, re-entering your password.
4. Network Troubleshooter: Your Digital Sherlock Holmes
Windows 7 has a built-in Network Troubleshooter. It's like your digital Sherlock Holmes, sniffing out the root of the problem.
- How to use it:
- Click the network icon in the system tray (the little computer monitor icon, usually near the clock).
- Click on "Troubleshoot problems."
- Let Windows do its thing. It'll attempt to diagnose and fix any issues it finds. The results can vary, but hey, it's worth a try!
5. The DHCP Debacle: Understanding IP Addresses
Think of your IP address like the postal code for your laptop on the internet. If it's not set up correctly, your laptop won't get where it needs to go. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is what usually assigns these addresses automatically. However, if DHCP is failing, your laptop might not get an IP address.
- Checking your IP settings:
- Go to Network and Sharing Center.
- Click "Change adapter settings."
- Right-click on your wireless adapter and choose "Properties."
- Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties."
- Make sure "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected. If not, change these and click "OK."
6. Firewall Fury: Does Windows Firewall Threaten the WiFi?
Sometimes, your own security measures can backfire. The Windows Firewall, meant to protect you, might inadvertently be blocking your WiFi connection.
- Checking your firewall settings:
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Firewall.
- Click on "Allow a program or feature through Windows Firewall."
- Ensure your wireless network adapter is checked and allowed. If it's not, change the settings to allow your wireless adapter.
7. Wireless Mode Mayhem: Selecting the Right Standard
Your router speaks a language. Your laptop must speak the same language! Wireless standards (like 802.11b/g/n) dictate the way your devices communicate. If your laptop and router aren't speaking the same language, you’ll experience problems.
- Checking your wireless mode: This often requires you to log into your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser – you can find this on a sticker on the router or in your router's manual). Look for the wireless settings and make sure it hasn't accidentally been set to a mode your laptop doesn't support. Often, "mixed mode" is the best option for compatibility.
8. Channel Surfing: Avoiding Wireless Interference
Think of your WiFi as a radio station. Different stations (or "channels") broadcast on different frequencies. If your neighbors' routers are using the same channel as yours, you'll experience interference.
- Changing your router's channel: Log into your router and look for wireless settings. Change the channel to one that's less congested. Many routers can automatically select the best channel for you.
9. Power Saving Puzzles: Balancing Battery Life and Connectivity
Windows 7, in its quest to conserve battery life, sometimes gets a little too enthusiastic, strangling the WiFi signal.
- Disabling power saving for your wireless adapter:
- Similar to the driver update instructions in section two, navigate to "Device Manager."
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click on your wireless adapter and select "Properties."
- Go to the "Power Management" tab and uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
10. The Router's Role: Is Your Router the Real Culprit?
Your router is the gatekeeper of your internet connection. If it's old, overloaded, or malfunctioning, it could be the source of your WiFi woes.
- Troubleshooting your router: Try restarting it (again!). Consider updating its firmware (check the manufacturer's website for instructions). If it's ancient, it might be time for an upgrade!
11. Encryption Enigmas: Ensuring the Right Security
Make sure you’re using a secure encryption method (WPA2 or WPA3 are best). Also, double-check your password! We've all done it – typed the wrong password a dozen times.
12. Resetting Network Settings: A Fresh Start
If all else fails, you can try resetting your network settings. This will remove and reinstall your network adapters.
- How to reset network settings:
- Click "Start," then type "cmd" in the search box. Right-click on "cmd.exe" and select "Run as administrator."
- Type the following commands one at a time, pressing Enter after each.
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip resetipconfig /releaseipconfig /renewipconfig /flushdns
- Restart your computer.
13. Hardware Hassles: The Physical Side of Connectivity
Sometimes, the problem isn't software, it's hardware. Your wireless adapter might be failing. Try to connect to a different WiFi network to see if your problem persists. If it does, you may have hardware problems.
14. The Nuclear Option: Performing a System Restore
If you've made recent changes to your system (like installing new software or drivers) and your WiFi issues started afterward, a System Restore could be your savior. This will revert your system to a previous state.
- How to use System Restore:
- Click "Start," type "System Restore" in the search box, and open it.
Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop

By IT Magics Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop by IT Magics
Wireless Network Connection Enabled but Not connected Fix Windows 7
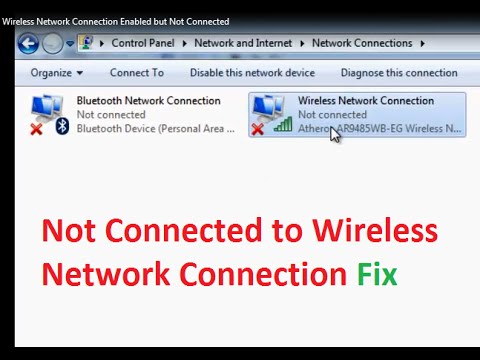
By troubleshooterrors Wireless Network Connection Enabled but Not connected Fix Windows 7 by troubleshooterrors
Cara Mengatasi Laptop Tidak Bisa Connect Wifi Windows 10, 8 & 7
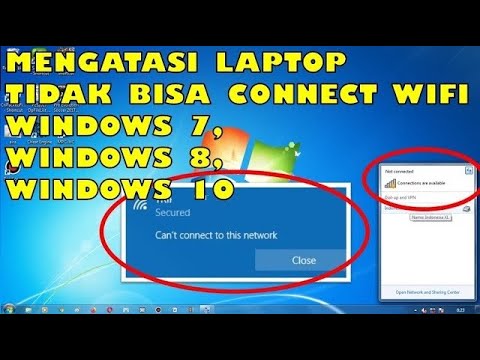
By Jari Mungil Rayyan Cara Mengatasi Laptop Tidak Bisa Connect Wifi Windows 10, 8 & 7 by Jari Mungil Rayyan

Title: 4 Cara Mengatasi WIFI Not Connected Pada Windows 7 8 10 Part 2
Channel: ZAINURI CHANNEL
4 Cara Mengatasi WIFI Not Connected Pada Windows 7 8 10 Part 2 by ZAINURI CHANNEL
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Fix Your Laptop Connection NOW!
WiFi Nightmare on Windows 7? Fix Your Laptop NOW!
Navigating the digital landscape with a consistently unreliable WiFi connection on your Windows 7 laptop can feel like a constant exercise in frustration. One moment you’re effortlessly streaming your favorite shows, and the next, you’re staring at a buffering wheel or, worse, a complete disconnection. We understand the urgency and the annoyance. This guide is designed to swiftly help you diagnose, and more importantly, resolve these WiFi woes and get your Windows 7 laptop back online and performing at its best. We won’t waste your time with generalities; we offer actionable, step-by-step solutions crafted to deliver results. Prepare to reclaim your connection and conquer those WiFi nightmares once and for all.
Diagnosing the WiFi Problem: Pinpointing the Culprit
Before diving into solutions, accurate diagnosis is paramount. Understanding the root of the problem will save considerable time and effort. Let’s systematically explore several common culprits behind frustrating WiFi inconsistencies.
1. Hardware Troubles: Checking Your Wireless Network Adapter
The first point of investigation is your laptop's wireless network adapter itself. It’s the hardware component responsible for receiving and transmitting WiFi signals. Sometimes, the problem isn't the WiFi network, but rather the adapter's communication with your system.
Device Manager Check: Open Device Manager (search for it in the Start Menu) and expand "Network adapters." Look for your wireless adapter. If it has an exclamation mark or a down arrow icon, it indicates a problem. An exclamation mark suggests a driver conflict or error, while a down arrow signifies the adapter is disabled. In either case, right-click the adapter.
- If disabled, select "Enable."
- If an exclamation mark is present, choose "Update driver software." Let Windows search online for an updated driver. If that doesn't work, try uninstalling the adapter and restarting your laptop; Windows should automatically reinstall it.
Physical Inspection: Ensure your laptop's WiFi switch (often a physical button on the side or front) is turned on. It's surprisingly easy to overlook this simple, yet crucial, step.
2. Software Conflicts: Identifying Driver Issues and Interference
Software, specifically drivers and interference with other programs, can often cripple a WiFi connection.
- Driver Rollback: If you recently updated or installed a new driver for your wireless adapter, it might be the source of your troubles. Return to the driver’s previous version. In Device Manager, right-click the adapter, go to "Properties," then "Driver." If the "Roll Back Driver" button is active, click it.
- Antivirus Interference: Some antivirus programs are overly aggressive and may block or interfere with network communication, including WiFi. Temporarily disable your antivirus software and test your connection. If the WiFi now works, you’ve identified a potential conflict. You may need to adjust the antivirus settings to allow network traffic or switch to a less intrusive security solution.
- Background Applications: Certain background applications can hog network resources, thereby affecting your WiFi performance. Close non-essential programs one by one and monitor your connection quality. Task Manager (accessed by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc) is an invaluable tool here; sort processes by network usage to see which programs are consuming the most bandwidth.
3. Router-Related Problems: Evaluating Signal Strength and Router Firmware
The WiFi router, the gateway to your internet connection, is another critical area for examination.
- Signal Strength Assessment: The distance between your laptop and the router, alongside structural obstructions like walls, significantly impacts signal strength. As a rule, position your laptop closer to the router. Windows 7 offers a built-in signal strength indicator (represented by bars in the system tray). The more bars, the stronger the signal. If the signal is weak, try moving your laptop, or consider a WiFi range extender to increase coverage.
- Router Firmware Update: Outdated router firmware can lead to various connectivity problems, including intermittent WiFi dropouts. Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing the router's IP address—often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1—into your web browser, then entering your router's username and password). Locate the firmware update section and follow the instructions to update to the latest version.
- Router Reboot: Sometimes, a simple reboot can resolve temporary glitches within the router. Unplug the router and modem for at least 30 seconds, then plug the modem back in first, waiting for it to fully initialize, and then plug in the router.
4. Internet Service Provider (ISP) Issues: Investigating External Factors
Sometimes, the problem isn't your equipment but rather the wider internet connection.
- Service Outage Check: Contact your ISP to determine if there's a known outage in your area. ISPs often update their websites with current service updates.
- Speed Test: Run an online speed test (like the one at Speedtest.net) to verify if you are receiving the bandwidth you are paying for. If the speeds are dramatically lower than expected, contact your ISP for troubleshooting support.
- Modem Check: While less common, problems with your modem can also cause WiFi issues. Try a power cycle of the modem (unplug it for 30 seconds and plug it back in).
Step-By-Step Solutions: Implementing Effective Fixes
Now that we've considered the potential causes, let's implement the most effective fixes.
1. Restarting Your Windows 7 Laptop and Refreshing Network Settings
A simple restart often resolves temporary software glitches.
Restart Windows 7: Simply shut down and then restart your laptop. This closes all running processes and clears temporary files, providing a fresh start for your operating system.
Flush DNS: In the search bar, type "cmd." Right-click on "Command Prompt" and select "Run as administrator." In the command prompt window, type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
ipconfig /flushdnsipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew
These commands flush your DNS cache, release your current IP address, and then renew it, which can address certain connectivity issues. Restart your system.
2. Configuring the Wireless Network Adapter Settings
Fine-tuning the settings of your wireless adapter can dramatically improve performance.
- Adapter Properties: In Device Manager, right-click your wireless adapter, then go to "Properties." Navigate to the "Advanced" tab.
- Adjust Settings:
- 802.11n Channel Width: Set this to "20 MHz Only" if you are experiencing connectivity problems, particularly if you are in a crowded WiFi environment. A narrower channel width can improve stability.
- Power Saving Mode: Disable power-saving features, which can sometimes interfere with the connection. Set this to "Maximum Performance."
- Roaming Aggressiveness: Experiment with different settings. Lower settings can reduce the aggressiveness with which the adapter searches for other access points, which might improve stability if you're not actively roaming between access points.
- * Antenna Diversity: Set this to "Auto" unless you know what you are doing.
3. Correcting Network Settings: TCP/IP Reset
Occasionally, the TCP/IP configuration can become corrupted. Resetting it is an effective solution.
Command Prompt: Open Command Prompt as an administrator (search for it in the Start Menu).
Enter the following commands: Type each of the following commands and press Enter after each line:
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip resetipconfig /flushdns
Restart your laptop.
4. Troubleshooting Wireless Network Profiles
Sometimes, an improperly configured or corrupted WiFi profile is the culprit.
- Remove the Network Profile: Open "Network and Sharing Center" (searched in the Start Menu). Click "Manage wireless networks."
- Remove and Reconnect: Delete the problem WiFi network. Then, reconnect to it by entering the network password. This will create a new, clean profile.
5. Consider Alternative Networking Strategies
If WiFi problems persist, consider these alternatives.
- Hardwired Connection: If feasible, use an Ethernet cable to connect your laptop directly to your router. This immediately bypasses any WiFi-related issues and provides a stable and often faster connection.
- WiFi Adapter Alternative: If your laptop's built-in wireless adapter is consistently problematic, consider purchasing a USB WiFi adapter as a replacement. These are inexpensive and can provide a more reliable connection.
Final Considerations and Ongoing Maintenance
Addressing WiFi issues is sometimes an ongoing process. Following these best practices ensures long-term reliability:
- Regular Driver Updates: Keep your wireless adapter drivers up-to-date. Visit the manufacturer's website for the latest versions.
- Password Protection and Security: Always use a strong password for your WiFi network to protect your connection.
- Router Placement: Place your router in a central, elevated location, away from walls and electronic devices that can cause interference.
- Schedule Periodic Router Reboots: Schedule a weekly or monthly router reboot to maintain optimal performance.
- Monitor your Connection: Keep an eye on the connection.
- Contact Tech Support: Don't hesitate to contact your ISP or a qualified computer technician for further assistance
