how to connect to wifi with windows 7 laptop

Title: How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7
Channel: MDTechVideos International
How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7 by MDTechVideos International
how to connect wifi to windows 7 laptop, how to connect wireless internet to windows 7 laptop, how to connect internet to windows 7 laptop, how to connect wifi to lenovo laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi to dell laptop windows 7, how to connect my laptop to wifi windows 7, how to connect acer laptop to wifi windows 7, how to connect toshiba laptop to wifi windows 7, how to connect laptop to wifi using windows 7, how to connect your laptop to wifi windows 7
Windows 7 Wi-Fi Nightmare? Solved! (Easy Fix Inside)
Windows 7 Wi-Fi Woes Vanquished! (Finally!)
Remember those days? The agonizing wait, the buffering, the signal that vanished faster than a magician's rabbit. Yes, we're talking about the Windows 7 Wi-Fi experience. Moreover, it could be a real test of patience. Furthermore, for many, it was a daily struggle. However, don't despair! Because the Wi-Fi woes are over. Let’s delve in and revive your connection.
The Ghost in the Machine: Identifying the Culprit
First off, let's acknowledge something. Technology has its quirks. Moreover, Windows 7, though a dependable operating system, did have its Wi-Fi gremlins. Consequently, it seemed that every user experienced connectivity problems with it. The diagnosis is crucial. Therefore, the first task is to identify the source of your frustration. Are you experiencing frequent disconnections? Is the signal strength fluctuating wildly? Moreover, is your connection painfully slow? These are all vital clues.
Digging into Devices: The Router Angle
Consequently, we need to cast our gaze towards your router. Indeed, it is your gateway to the internet. However, sometimes your router can be the issue. So, you should start by restarting it. Generally, this simple step resolves a surprising number of issues. Also, you should verify your router's firmware is updated. Outdated firmware can cause compatibility problems. Furthermore, your router's location matters. To that end, walls, electronics, and other obstructions can interfere with the signal.
Drivers: The Silent Champions of Connection
Next, let's explore drivers. Specifically, drivers are essential software components. They allow your computer to "talk" to your Wi-Fi adapter. Moreover, outdated or corrupted drivers are major causes of Wi-Fi problems. So, check your Wi-Fi adapter's driver. Make sure it’s the latest version. You can do this through Device Manager. Simply right-click the adapter and select "Update driver." Indeed, it is often the solution to many problems.
Security Settings: Guarding Your Network
Your security settings often play a huge role. WEP, an older security protocol, is not secure anymore. Consequently, it could cause connectivity issues. So, consider upgrading to WPA2 or WPA3. Meanwhile, ensure your network password is secure and complex. That prevents unauthorized access and potential interference.
The Power Plan Puzzle: Balancing Performance
Moreover, Windows 7's power plan settings could impact Wi-Fi. For example, your computer might be turning off your Wi-Fi adapter to save power. Therefore, you should adjust your power plan. First, access your power options in Control Panel. Second, set your Wi-Fi adapter to operate at maximum performance. This simple change can sometimes significantly improve your connection.
Channel Surfing: Finding the Sweet Spot
Did you know that Wi-Fi routers operate on different channels? Furthermore, some channels might be more congested than others. Therefore, you should experiment with different channels. Access your router's settings. Then, try changing the Wi-Fi channel. This could minimize interference from neighboring networks.
Troubleshooting with Precision: The Windows 7 Toolkit
Windows 7 includes built-in troubleshooting tools. Moreover, these tools can often identify and fix common Wi-Fi problems. So, access the Network and Sharing Center. Then, select "Troubleshoot problems." The troubleshooter will guide you through potential solutions. Therefore, utilize this tool.
The Unsung Hero: Network Adapter Properties
Another way you can fix your Wi-Fi problems is by editing network adapter properties. Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter in Device Manager. Select "Properties." Go to the "Advanced" tab. In addition, you can make certain adjustments. For example, consider optimizing the "Wireless mode" setting. You should modify the transmit power settings appropriately.
When All Else Fails: Seeking Expert Help
If you try these steps, and still struggle, then seek assistance. Consult with a tech-savvy friend. Furthermore, consider contacting your internet service provider. They can often diagnose and resolve complex issues.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Seamless Connectivity
Finally, you have solutions at your disposal. You can conquer your Windows 7 Wi-Fi woes. Now, your internet experience should be smooth sailing. Then, enjoy a fast and reliable connection. So, go forth and browse, stream, and connect with confidence. The Wi-Fi nightmare is over!
Laptop WiFi Dying? This ONE Trick Boosts Your Signal INSTANTLY!Windows 7 Wi-Fi Nightmare? Solved! (Easy Fix Inside)
Hey there, fellow tech travelers! Remember those days when connecting to the internet on your trusty Windows 7 machine felt like wrestling an octopus in a phone booth? The constant dropouts, the cryptic error messages, the sheer frustration… We've all been there! It’s a memory etched in the digital tapestry of our lives, a blend of nostalgia and barely-contained rage. But before you start reminiscing about chucking your laptop out the window, breathe easy! We're diving deep into the heart of the Windows 7 Wi-Fi woes and emerging victorious. Forget expensive IT consultants – consider this your personal, pocket-sized tech guru, ready to banish those Wi-Fi gremlins once and for all!
1. The Windows 7 Wi-Fi Struggle is Real (and We Get It!)
Let's be honest, Windows 7 was a champion. It served us well, gracefully navigating the early days of the internet evolution. But, like a seasoned marathon runner, it started to show its age when it came to modern Wi-Fi standards. We remember spending hours poring over forums, desperately searching for a fix, a digital lifeline in a sea of dropped connections. The intermittent Wi-Fi could be compared to a whimsical song on a faulty old radio – sometimes you hear a lovely melody, and sometimes it's nothing but static. We felt the pain, and we're here to tell you: you’re not alone!
2. Understanding the Culprits: What Went Wrong with Windows 7 Wi-Fi?
Before we wield our digital magic wands, let’s understand the enemies we face. What's causing this Wi-Fi havoc? The primary culprits often include outdated drivers, incompatibility with modern Wi-Fi routers, and sometimes, just plain old software glitches. Imagine your Wi-Fi adapter as a translator trying to communicate with a router speaking a language it barely understands. The results can be messy. Think of it as your Wi-Fi adapter simply not speaking the same language as the router anymore – a classic case of a communication breakdown!
3. Driver Dilemma: The First Frontier in Fixing Wi-Fi
The most common starting point is always the drivers. Drivers are essentially the instructions that tell your Wi-Fi adapter how to "speak" to your router. Outdated drivers are like trying to navigate with an ancient map – you’re likely to end up lost and frustrated.
3.1 Finding Your Wi-Fi Adapter's Name
The first step is identifying your Wi-Fi adapter's name. This is like knowing your enemy's name before you charge into battle. Here's how:
- Click the Start button.
- Right-click on Computer and select Manage.
- Click on Device Manager in the left-hand pane.
- Expand Network adapters.
- You'll find your Wi-Fi adapter listed there. The name will usually include terms like “Wireless Network Adapter” or “Wi-Fi Adapter.” Jot it down.
3.2 Hunting Down the Latest Drivers
Now comes the detective work. We need the most current drivers for your adapter.
Manufacturer’s Website: The best place to find drivers is the manufacturer's official website (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, Realtek). Search for your adapter model and download the latest Windows 7 drivers. Think of it like going to the source.
Device Manager (Again!): You can also try updating the drivers directly through Device Manager. Right-click your adapter, select "Update driver software," and choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." This is the equivalent of a quick scan for a minor problem.
4. Router Rumble: Ensuring Compatibility
Sometimes, the problem isn't your computer, but your router. Modern routers often use standards that Windows 7’s Wi-Fi adapter might struggle with.
Check Your Router's Settings: Make sure your router isn't set to a Wi-Fi standard (like 802.11ac) that your Windows 7 adapter can't handle. Try switching it to 802.11g or 802.11n, which are generally more compatible with older systems. It's like slowing down the conversation so everyone can understand.
Router Firmware: An outdated router's firmware can cause compatibility issues. Check your router's manual for instructions on updating the firmware.
5. Power Saving Shenanigans: The Hidden Wi-Fi Thief
Windows 7, by default, sometimes uses power-saving settings that can cripple your Wi-Fi connection. It's as though it's trying to conserve energy from your internet connection, unknowingly hampering its flow.
- Go back into Device Manager (see step 3.1).
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select Properties.
- Click on the Power Management tab.
- Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This is like giving your Wi-Fi a constant supply of energy.
6. Firewall Fiascos: Are You Blocking the Connection?
Your firewall, designed to protect you, can sometimes accidentally block the Wi-Fi connection. Like a overzealous security guard, it might be a bit too eager to keep things under control.
- Check Your Firewall Settings: Make sure your firewall (Windows Firewall, or any third-party firewall you might have installed) isn't blocking your Wi-Fi adapter or the network connection.
7. Network Reset: The Digital Restart Button
Sometimes, a simple reset is all it takes. We can all appreciate a quick reset.
- Forget and Reconnect to Your Network: In the Network and Sharing Center (accessible via the Control Panel), "forget" your Wi-Fi network and then reconnect to it. This is like restarting your computer, but for your network connection.
8. IP Address Troubles: The Missing Address
Sometimes, your computer isn't getting a proper IP address from your router.
- Renew Your IP Address: Open the “Run” dialog box (Windows Key + R), type
cmd, and press Enter. In the command prompt, typeipconfig /releaseand press Enter, followed byipconfig /renewand press Enter. This is like asking for a new address to be delivered.
9. Malware Mayhem: A Hidden Wi-Fi Saboteur
Viruses and malware can, in some cases, mess with your network settings and disrupt your Wi-Fi.
- Run a Scan: Perform a full system scan with your antivirus software. Think of it as a digital cleaning of your home.
10. Troubleshooting Tools: Windows 7's Secret Weapons
Windows 7 comes with built-in troubleshooting tools that can often diagnose and fix Wi-Fi problems.
- Network Troubleshooter: Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray and select "Troubleshoot problems." This is like consulting the doctor for a quick checkup.
11. Hardware Hurdles: Checking the Physical Connection
Sometimes, the issue is physical.
- Check the Adapter: Make sure your Wi-Fi adapter is properly installed.
12. Wireless Interference: External Factors
Wi-Fi signals are delicate creatures, susceptible to interferences from other devices.
- Microwave and Cordless Phones: These can interfere with the 2.4GHz band. Try switching your router to the 5GHz band if possible.
13. Reinstalling Your Wi-Fi Adapter
If all else fails, consider reinstalling your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Uninstall and Reinstall: Go into Device Manager, uninstall your adapter. Then, restart your computer, it will usually auto-install.
14. The Nuclear Option: System Restore
As a last resort, you can try a system restore to a point before the Wi-Fi problems started.
- System Restore: In the Control Panel, search for "Recovery" and choose "Open System Restore."
15. Celebrate Success: You Did It!
Congratulations! You've navigated the treacherous terrain of Windows 7 Wi-Fi problems. You've conquered the digital gremlins and are back online. Now go forth and stream, browse, and connect with confidence!
Wrapping It All Up!
So, there you have it! A complete guide to slaying the Windows 7 Wi-Fi dragon. We've covered everything, from driver updates and router settings to power-saving tricks and troubleshooting tools. Each step, like a piece of a puzzle, will build into a complete picture. We truly hope this has helped and that you’re back online in no time. It’s a feeling of digital freedom!
Image Alt Text: A smiling person celebrating after fixing their Windows 7 Wi-Fi connection, surrounded by triumphant emojis.
Image Caption: Victory! No more Wi-Fi woes on your old Windows 7 machine!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why is my Windows 7 Wi-Fi so slow? The most common culprits are outdated drivers, router compatibility issues, and network congestion. Go through the steps listed above and troubleshoot them.
- How do I find my Wi-Fi password on Windows 7? If you're connected to the network, go to the
Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop

By IT Magics Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop by IT Magics
How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
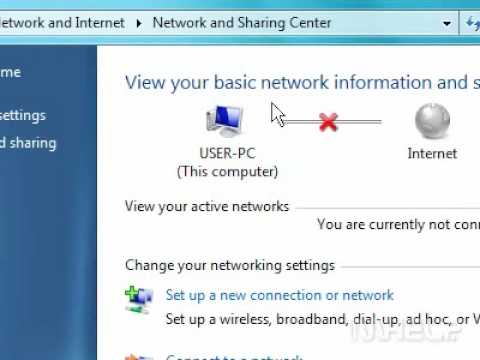
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U
Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop
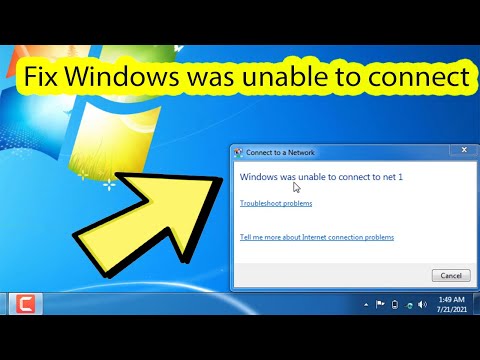
By IT Magics Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop by IT Magics

Title: How to turn on wifi in windows 7
Channel: Being Selftech
How to turn on wifi in windows 7 by Being Selftech
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
Windows 7 Wi-Fi Nightmare? Solved! (Easy Fix Inside)
The frustration. The exasperation. The seemingly endless cycle of dropped connections, slow speeds, and the gnawing feeling that your Wi-Fi is conspiring against you: these are the hallmarks of the Windows 7 Wi-Fi "nightmare" that has plagued countless users for years. But breathe easy. We’ve navigated the digital trenches, battled the bandwidth bottlenecks, and emerged victorious. We’ve compiled a definitive guide – a roadmap to a flawlessly functioning wireless connection on your Windows 7 machine. Prepare to bid farewell to Wi-Fi woes and embrace a world of seamless streaming, effortless browsing, and lag-free gaming.
Identifying the Root of the Problem: Common Windows 7 Wi-Fi Culprits
Before wielding the digital tools of the trade, it’s crucial to understand the enemy. The erratic behavior of Wi-Fi on Windows 7 often stems from a combination of factors, not just a single, solitary gremlin. Consider these prevalent troublemakers:
Outdated Wireless Drivers: This is arguably the most common cause. Hardware manufacturers constantly release updated network drivers to optimize performance, address security vulnerabilities, and ensure compatibility with the latest wireless standards. Failing to keep these drivers current is akin to driving a race car with flat tires.
Incorrect Network Configuration: From the simplest of settings to complex IP address assignments, a misconfigured network can send your Wi-Fi connection spiraling into a chaotic vortex of dropped packets and frustrating delays.
Interference and Congestion: The airwaves are a crowded place, and your wireless signal is constantly vying for attention. Interference from other devices, such as microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks, can severely impact your connection strength and stability.
Power Management Settings: Windows 7's power management features, designed to conserve battery life on laptops, can inadvertently throttle your Wi-Fi adapter, leading to intermittent disconnections and reduced speeds.
Security Protocol Incompatibilities: Older security protocols, like WEP, are outdated and susceptible to vulnerabilities, and may cause connection issues with modern routers. Ensure your router uses a robust, secure protocol such as WPA2 or WPA3.
Hardware Malfunctions: While less common, a faulty wireless adapter or a damaged router antenna can also contribute to the problems. These require a more hands-on approach to solve.
The Ultimate Windows 7 Wi-Fi Troubleshooting Toolkit
Now that we've identified the usual suspects, let's arm ourselves with the tools needed to solve the Windows 7 Wi-Fi "nightmare." We'll systematically address each potential issue, providing clear and actionable steps that even the most novice user can follow.
Step 1: Updating Your Wireless Network Adapter Drivers
This is the cornerstone of a stable Wi-Fi connection. Outdated drivers are the single most frequent cause of Wi-Fi problems. Here’s how to update them:
- Access Device Manager: Click the Start button, type "Device Manager" into the search box, and press Enter.
- Locate Your Network Adapter: In the Device Manager window, expand the "Network adapters" category. You'll see a list of all the network adapters installed on your computer. Identify your wireless network adapter – it will usually have a name that indicates its function (e.g., "Intel Wireless-N 7260").
- Update the Driver: Right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Update driver software."
- Choose Your Update Method: You'll be presented with two options:
- Search Automatically for Updated Driver Software: Windows 7 will attempt to locate and install the latest driver from Microsoft's online database. This is the easiest method, but it might not always find the newest driver.
- Browse My Computer for Driver Software: If you've already downloaded the driver from the manufacturer's website (which is generally the preferred method), select this option and browse to the location of the downloaded driver files.
- Follow the On-Screen Instructions: Complete the driver installation process. You may need to restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Pro Tip: Visit the website of your wireless network adapter manufacturer (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, Realtek). Download the latest driver specifically for your adapter model and Windows 7 version from there. This ensures you have the most up-to-date and optimized driver.
Step 2: Network Adapter Power Management Tweaks
Windows 7's default power management settings can sometimes interfere with Wi-Fi performance. By adjusting these settings, we can prevent Windows from throttling your adapter.
- Return to Device Manager: Follow the first two steps in "Step 1" above to return to the Device Manager and locate your wireless network adapter.
- Access Properties: Right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Properties."
- Navigate to Power Management: In the Properties window, go to the "Power Management" tab.
- Disable Power Saving: Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- Apply and Restart: Click "OK" and then restart your computer.
This adjustment prevents Windows from putting your Wi-Fi adapter into a low-power state, which can cause connection drops.
Step 3: Diagnosing and Resolving Network Configuration Problems
A well-configured network is essential for smooth Wi-Fi operations. Windows 7 offers built-in tools to diagnose and often repair network problems.
- Open the Network and Sharing Center: Click the Start button, then select "Control Panel." From there, click "Network and Internet," and then "Network and Sharing Center."
- Troubleshoot Connection Issues: In the Network and Sharing Center, click "Troubleshoot problems." Select the appropriate trouble-shooting option relevant to your connection. Windows will then attempt to automatically diagnose and resolve any detected network issues, guiding you with on-screen prompts.
- Manually Configure TCP/IP Settings (If Necessary): If the automatic troubleshooting doesn’t work, you may need to manually configure the TCP/IP settings. Right-click on your wireless network connection in the Network and Sharing Center and select "Properties". Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties."
- Make sure "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected (unless your network requires a static IP address).
- If you still experience connection problems, try manually entering the DNS server addresses. Google's public DNS servers (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) are often a good starting point.
Step 4: Minimizing Interference and Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Environment
Even with the correct drivers and proper configuration, interference can still wreak havoc on your Wi-Fi connection. Implementing a few strategies can dramatically improve signal quality and stability.
- Relocate Your Router: Place your router in a central location within your home, away from walls and obstructions. The fewer barriers between your router and your devices, the stronger and more reliable the signal will be.
- Reduce Wireless Interference:
- Microwaves: Operate microwaves away from the router as they emit frequencies that can interfere with Wi-Fi.
- Other Wireless Devices: Move Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, and other electronics away from your router.
- Neighboring Wi-Fi Networks: Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app (available for smartphones) to identify the least congested Wi-Fi channel in your area. Change your router's channel settings to the least crowded channel.
- Consider a Wi-Fi Extender: If you have a large home or experience dead spots, consider using a Wi-Fi extender or mesh network system to boost your signal range.
Step 5: Wireless Security Protocol Verification
Outdated wireless security protocols can lead to connection instability and vulnerabilities. Always ensure your router and connection use up-to-date security standards.
- Access Your Router Administration Page: Open a web browser and type your router's IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into the address bar. You'll need your router's username and password to log in.
- Navigate to the Wireless Security Settings: Locate the section in your router's settings that deals with wireless security, usually under the "Wireless" or "Security" tab.
- Select WPA2 or WPA3: Ensure your router is using WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) or the more recent WPA3 security protocol. These offer robust encryption and protection. Avoid using the older WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) protocol, as it’s highly insecure.
- Set a Strong Password: Create a strong, complex password for your Wi-Fi network. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips and Considerations
While the above represents the most common solutions to Windows 7 Wi-Fi problems, here are a few more tips to help you tackle more difficult or nuanced situations:
- Reset Your Router: A simple router restart can often resolve temporary glitches. Unplug your router for 30 seconds, then plug it back in. Wait for it to fully restart before attempting to connect.
